Abstract
A number of clinical trials are evaluating immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with AML/MDS with encouraging results (Daver N et al, EHA 2017; Garcia-Manero et al, EHA 2017). Approximately 5-10% of patients with leukemia treated with checkpoint inhibitors had immune related adverse event (irAE) of pneumonitis, one of the life-threatening irAEs. Increased awareness, distinction from infectious pneumonia, and early intervention are critical in the management of pneumonitis-irAEs in patients with leukemia. Especially in the setting of acute leukemia the ability to distinguish immune mediated pneumonitis from infectious pneumonia is critical to determine whether or not the addition of high-dose steroids is warranted. The mechanisms of pneumonitis-irAE, the most important step for risk stratification and early detection remain elusive.
Methods
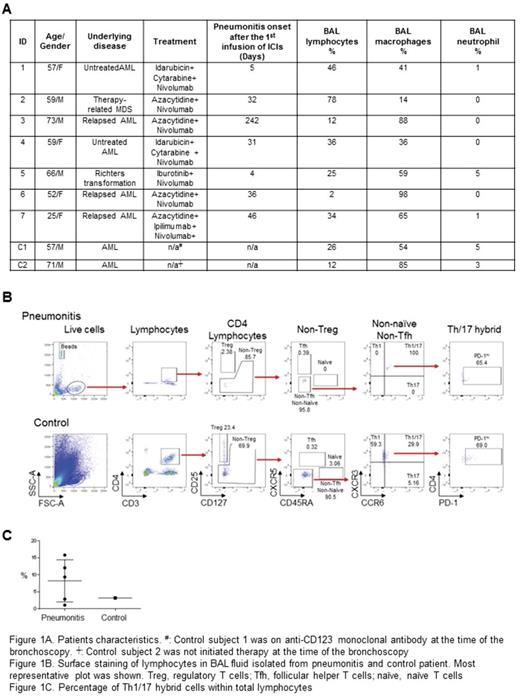
We collected bronchial alveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from seven leukemia patients (6 AML/MDs and 1 Richter transformation) who received checkpoint inhibitor based therapy on clinical trials, and subsequently developed respiratory symptoms and had a bronchoscopy. As a control, we collected BAL fluid from two AML/MDS patients who had never received checkpoint inhibitor therapy. We stained BAL CD4 T cell with lineage specific surface markers using the following antibodies; anti-CD4 BUV396, anti-CXCR3 BV 421, anti-CD45RA BV786, anti-CD3 PerCP, anti-CCR6 FITC, anti-CD25 PE, anti-PD-1 PE-Dazzle, anti-CXCR5 APC, and anti-CD127 APC 700. BAL CD4 T cell subsets, including Th1, 2, 17, follicular helper T, and regulatory T cells, were enumerated and the proportion and profile of the CD4 T cell subsets within the total lymphocytes were compared between pneumonitis group and control group.
Result
Patient demographics are described in Figure 1A. Mean age of the patients with pneumonitis-irAE was 56. Most of them were on nivolumab in combination with chemotherapy/hypomethylator therapy. The patients developed pneumonitis 52.7 ± 77.8 days (mean ± DS) after the first exposure to a checkpoint inhibitor. Compared to the control group, lymphocytes were expanded in pneumonitis group (% lymphocytes, disease versus control: 32.3% vs. 19.0%). This observation led us to further characterize the lymphocytes in available BAL samples, especially CD4 T cells given their central role in immune efficacy and toxicity. Interestingly, Th1/17 hybrid cells (CXCR3hi CCR6hi), known to be pathogenic in autoimmune diseases, were expanded in the pneumonitis group compared to the control (8.24 % vs 3.19 %) (Figure 1B and C) These Th1/17 hybrid cells express high level of PD-1, suggesting their hyperactive status. Although premature, there was a trend that regulatory T cells were decreased in pneumonitis group (Data not shown). Surface staining of CD4 T cells in BAL fluid revealed that both disease and control had no follicular helper T cells, the CD4 T cell subset governing humoral immunity. Consistently, B cells were barely detected in BAL in both groups (Data not shown).
Conclusion
These results suggest the possibility of increased Th1/17 hybrid cells with decreased Tregs as a biomarker of pneumonitis. The high PD-1 expression on Th1/17 hybrid cells suggests activation (or exhaustion) in the lungs in patients with irAEs. Further investigation of Th1/17 hybrid cells and correlation with peripheral blood may provide an insight into the mechanisms of pneumonitis-irAEs and biomarkers for early detection. In parallel, decreased Treg in the BAL may indicate an increased susceptibility to immune activation and inflammation seen in irAEs.
Kantarjian: Novartis: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding. Sharma: Jounce: Consultancy, Other: stock, Patents & Royalties: Patent licensed to Jounce; Evelo: Consultancy, Other: stock; Astellas: Consultancy; EMD Serono: Consultancy; Consetellation: Other: stock; Amgen: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Other: stock; Neon: Consultancy, Other: stock; BMS: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy. Daver: Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal